|
|
|
New Acropolis Museum Opens With Lavish Party |
|
By Nicholas Paphitis - Associated Press Athens, Greece Gods, heroes and long-dead mortals stepped off their plinths into the evening sky of Athens on Saturday during the lavish launch of the new Acropolis Museum, a decades-old dream that Greece hopes will also help reclaim a cherished part of its heritage from Britain. |
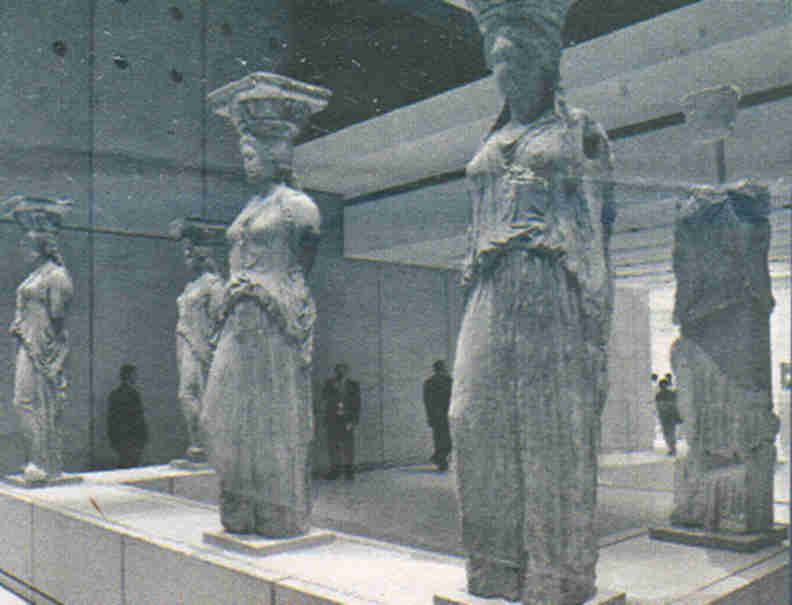 |
The nearly euro3 million ($4.1 million) opening ceremony was attended by some 400 guests, including European Commission President Jose Manuel Barroso, UNESCO Director-General Koichiro Matsuura, and foreign heads of state and government. Conspicuously, there were no government officials from Britain, which has repeatedly refused to repatriate dozens of 2,500-year-old sculptures from the Parthenon temple that are held in the British Museum. President Karolos Papoulias said Greeks think of the Acropolis monuments as their “identity and pride,” and renewed the demand for the missing marble works, displayed in London for the past 200 years. “The whole world can now see the most important sculptures from the Parthenon together,” Papoulias said. “Some are missing. It is time to heal the wounds on the monument by returning the marbles that belong to it.” Culture Minister Antonis Samaras said the sculptures “will inevitably return,” but ruled out Greece acknowledging the British Museum’s legal title to the works — as requested by officials in London as a precondition for any loan. Large crowds watched the heavily policed opening ceremony from nearby cafes, and families gathered on overlooking balconies. Crouching 300 yards from the Parthenon’s slender bones like a skewed stack of glass boxes, the euro130 million ($180 million) museum provides an airy setting for some of the best surviving works of classical sculpture that once adorned the Acropolis. By day, printed glass panels filter the harsh sunlight while revealing the ancient citadel in the background. The internal lighting projects the battered statues outward at night, contrasting with the floodlit ruins on the low hill. “We tried … to be as simple, as clear, as precise as we could be establishing a visual relation between the Parthenon, the museum with the beautiful sculptures and with the archaeological remnants,” said the building’s designer, French-Swiss architect Bernard Tschumi. And with a special glass hall designed to showcase all the surviving Parthenon sculptures in their original alignment, the building is Greece’s answer to the argument that it had nowhere to safely house those sawed off the temple in the early 1800s by British diplomat Lord Elgin. Among the exhibits are small sculptures recently returned from Italy, The Vatican and Germany. The Parthenon was built at the height of Athens’ glory, between 447-432 B.C., in honor of the city’s patron goddess, Athena, and is still considered one of the most impressive buildings in the world. |
|
|
(Posting date 24 July 2009) HCS encourages readers to view other articles and releases in our permanent, extensive archives at the URL http://www.helleniccomserve.com/contents.html. |
|
|
|
|
2000 © Hellenic Communication Service, L.L.C. All Rights Reserved.
http://www.HellenicComServe.com |
|